Cardiovascular Conditioning:
Cardiovascular fitness is fundamental for soccer players, as the sport involves continuous movement across the field for extended periods. To enhance their cardiovascular endurance, players engage in various forms of cardiovascular exercises such as running, cycling, and swimming. Interval training, which involves alternating between high-intensity bursts of activity and periods of rest or low-intensity activity, is particularly effective in simulating the intermittent nature of soccer matches.

Strength Training:
Soccer is a physically demanding sport that requires players to possess strength in their lower body, core, and upper body. Strength training exercises such as squats, deadlifts, lunges, and plyometrics are incorporated into players’ workouts to build muscle strength and power. Additionally, exercises targeting the core muscles, including planks, Russian twists, and medicine ball exercises, help improve stability and balance, crucial for executing precise movements on the field.

Speed and Agility Training:
The ability to accelerate quickly, change direction rapidly, and react swiftly to on-field situations is essential for soccer players. Speed and agility training drills, such as shuttle runs, ladder drills, cone drills, and agility ladder exercises, are integral components of a soccer player’s workout routine. These drills not only improve footwork and coordination but also enhance reaction times and agility, giving players a competitive edge during matches.
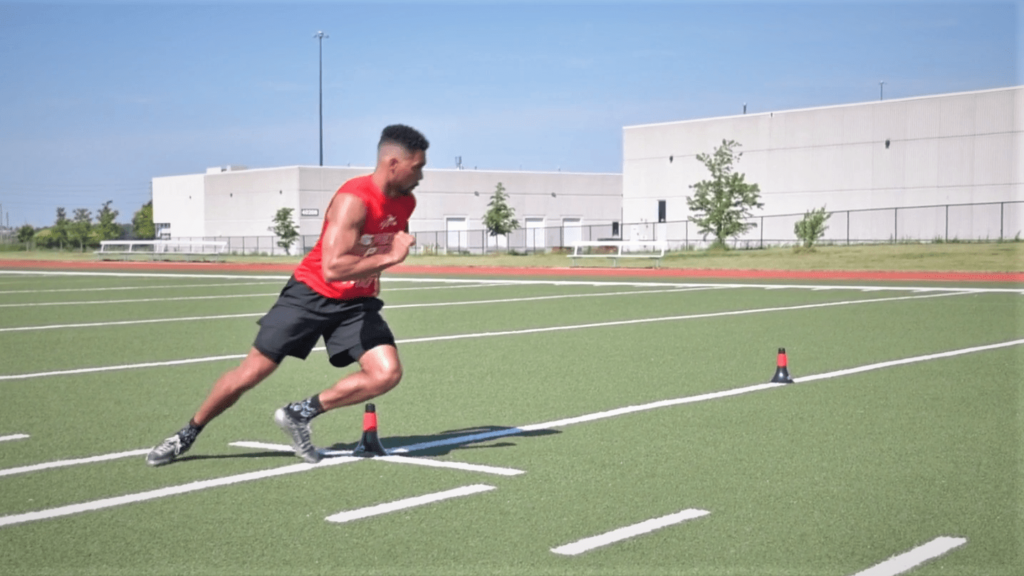

Flexibility and Mobility:
Maintaining optimal flexibility and mobility is vital for preventing injuries and maximizing performance on the soccer field. Stretching exercises, yoga, and mobility drills help soccer players improve their range of motion, loosen tight muscles, and reduce the risk of strains and sprains. Dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching after workouts aid in muscle recovery and promote overall flexibility.
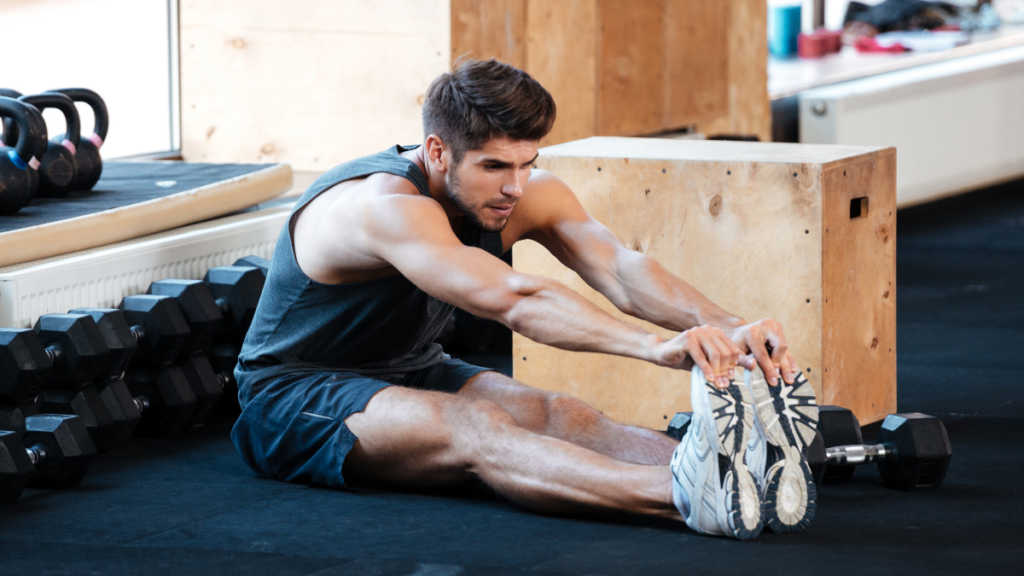

Plyometric Training:
Plyometric exercises, which involve rapid and explosive movements, are incorporated into soccer players’ training programs to improve power, speed, and jumping ability. Box jumps, depth jumps, bounding exercises, and medicine ball throws are examples of plyometric exercises that help enhance a player’s explosiveness and athleticism, enabling them to outmaneuver opponents and execute powerful kicks and headers during matches.
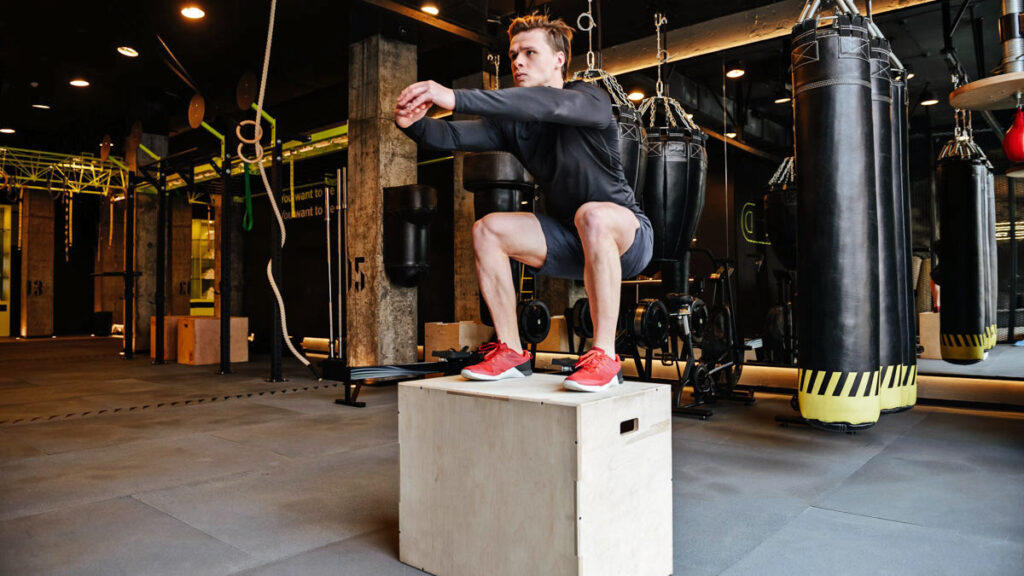

Endurance Training:
Soccer matches can be physically demanding, often lasting for 90 minutes or more, with players covering significant distances at varying intensities. Endurance training programs focus on building the aerobic capacity of players to sustain high levels of performance throughout the game. Long-distance runs, tempo runs, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions are commonly incorporated into players’ training schedules to improve their stamina and endurance.

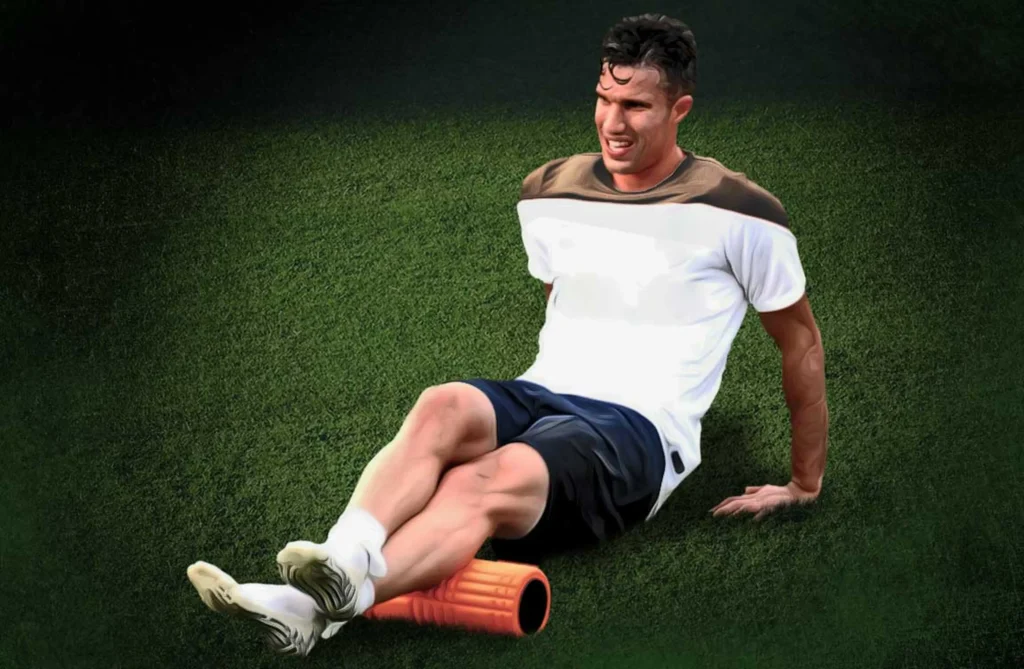
Recovery and Regeneration:
In addition to intense training sessions, adequate rest and recovery are crucial for soccer players to maintain peak performance and prevent overtraining injuries. Active recovery techniques such as foam rolling, massage therapy, ice baths, and contrast water therapy help alleviate muscle soreness, reduce inflammation, and promote faster recovery between training sessions and matches. Proper nutrition, hydration, and sleep are also essential components of the recovery process, allowing players to recharge both physically and mentally.

Professional soccer players undergo rigorous training regimens to achieve and maintain peak physical fitness levels required to excel in the sport. From cardiovascular conditioning and strength training to speed and agility drills, flexibility exercises, and plyometric workouts, every aspect of a player’s fitness is meticulously addressed to ensure optimal performance on the field. By combining dedicated training with proper nutrition, hydration, and recovery strategies, soccer players are able to meet the physical demands of the game and showcase their skills at the highest level of competition.